Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS technology offers high-precision positioning by correcting satellite signal errors in real-time. However, despite its advanced capabilities, users often encounter challenges that affect the accuracy and reliability of rtk gps systems. This article explores troubleshooting common RTK GPS errors and fixes to help users maintain optimal performance.
Understanding RTK GPS and Its Common Errors
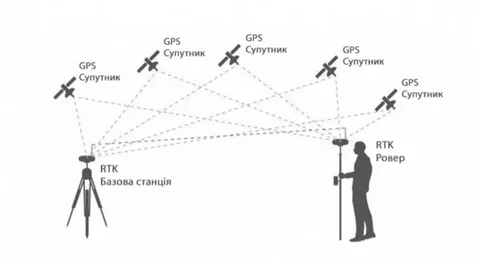
RTK GPS enhances standard GPS accuracy by using a base station to provide correction data to the rover unit. This method significantly reduces positioning errors, often achieving centimeter-level accuracy. However, several factors can cause errors in RTK systems, including:
- Signal interference or blockage
- Incorrect setup or calibration
- Poor satellite geometry
- Data link issues
Identifying these issues early is crucial for ensuring the RTK GPS system works efficiently.
Common RTK GPS Errors and How to Fix Them
1. Signal Interference and Multipath Errors
Problem: Signal interference from buildings, trees, or other obstructions can cause multipath errors, where GPS signals reflect off surfaces before reaching the receiver.
Fix:
- Position the base and rover stations in open areas with a clear view of the sky.
- Use high-quality antennas designed to minimize multipath effects.
- Avoid operating near large metal structures or dense foliage.
2. Data Link Failures
Problem: RTK relies on continuous communication between the base station and rover. If the data link fails due to radio interference or low signal strength, positioning accuracy degrades.
Fix:
- Check and adjust the radio frequency settings to avoid interference.
- Use repeaters or higher-powered radios to extend communication range.
- Regularly inspect and maintain antennas and cables.
3. Incorrect Base Station Coordinates
Problem: If the base station coordinates are inaccurate, the rover’s position data will be offset, causing errors in measurements.
Fix:
- Verify base station coordinates using known control points or established benchmarks.
- Perform static surveys to establish precise base station locations before RTK operation.
- Update base coordinates regularly if the base is moved.
4. Poor Satellite Geometry
Problem: Satellite geometry refers to the relative position of satellites in the sky. Poor geometry can degrade the quality of the RTK fix.
Fix:
- Use GPS receivers capable of multi-constellation tracking (e.g., GPS, GLONASS, Galileo) to increase available satellites.
- Schedule work during times when satellite geometry is optimal, based on satellite availability forecasts.
- Monitor dilution of precision (DOP) values and avoid working when DOP is high.
Best Practices for Troubleshooting Common RTK GPS Errors and Fixes
- Regular Calibration: Periodically calibrate equipment and verify system settings.
- Software Updates: Keep firmware and software updated to benefit from the latest fixes and improvements.
- Training: Ensure operators are well-trained on RTK system setup and troubleshooting.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed logs of issues and solutions to streamline future troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of troubleshooting common RTK GPS errors and fixes is essential for maximizing the accuracy and reliability of RTK GPS systems. By understanding the typical problems—from signal interference to data link failures—and implementing proven solutions, users can significantly enhance their positioning results and overall productivity in the field.